Chuck a single taxpayer earns 75000 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate financial landscape of a single taxpayer earning $75,000, providing invaluable insights and practical advice to help you navigate the complexities of tax implications, financial planning, and lifestyle choices.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the federal income tax brackets applicable to this income level, estimate the taxpayer’s federal income tax liability, and discuss potential tax deductions and credits that could reduce the tax burden. We will also delve into appropriate savings and investment strategies, provide guidance on budgeting and debt management, and emphasize the importance of starting retirement planning early.
Tax Implications for a Single Taxpayer Earning $75,000
A single taxpayer earning $75,000 falls within the 22% federal income tax bracket. This means that they will pay 22% of their income in federal income taxes.
Based on this tax bracket, the taxpayer’s estimated federal income tax liability is $16,500. However, this amount may vary depending on factors such as deductions and credits.
Potential Tax Deductions and Credits
- Standard deduction: $12,950 (2023)
- Itemized deductions: Mortgage interest, charitable contributions, state and local taxes
- Child tax credit: Up to $2,000 per qualifying child
- Earned income tax credit: For low- and moderate-income taxpayers
By utilizing these deductions and credits, the taxpayer can reduce their taxable income and potentially lower their tax liability.
Financial Planning Considerations
Savings and Investment Strategies
For a single taxpayer earning $75,000, it is crucial to establish a sound savings and investment plan. This may include:
- Emergency fund: Aim for 3-6 months of living expenses
- Retirement savings: Contribute to a 401(k) or IRA
- Short-term savings: For upcoming expenses or financial goals
- Investments: Consider a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and real estate
Budgeting and Debt Management
Effective budgeting and debt management are essential for financial stability. The taxpayer should:
- Create a monthly budget: Track income and expenses
- Reduce unnecessary expenses: Identify areas where spending can be cut
- Pay off high-interest debt first: Prioritize eliminating costly debt
- Consider debt consolidation: Explore options to lower interest rates
Retirement Planning
Starting retirement planning early is crucial. The taxpayer should:
- Contribute to a retirement account: Maximize tax-advantaged savings
- Estimate retirement expenses: Plan for a comfortable retirement lifestyle
- Seek professional advice: Consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance
Lifestyle and Spending Habits
Impact on Lifestyle
A salary of $75,000 provides a comfortable lifestyle for a single taxpayer. However, it is important to manage expenses wisely to maintain financial well-being.
Expense Management
The taxpayer should:
- Track expenses: Monitor spending to identify areas for improvement
- Negotiate bills: Explore ways to reduce expenses on utilities, insurance, and other services
- Shop around: Compare prices before making purchases
- Avoid impulse purchases: Make informed decisions before spending
Financial Goals and Spending Plan, Chuck a single taxpayer earns 75000
Setting financial goals and creating a spending plan are essential for financial success. The taxpayer should:
- Define financial goals: Short-term, mid-term, and long-term objectives
- Create a spending plan: Allocate funds based on financial goals and priorities
- Review and adjust regularly: Monitor progress and make adjustments as needed
Comparison to Other Income Levels
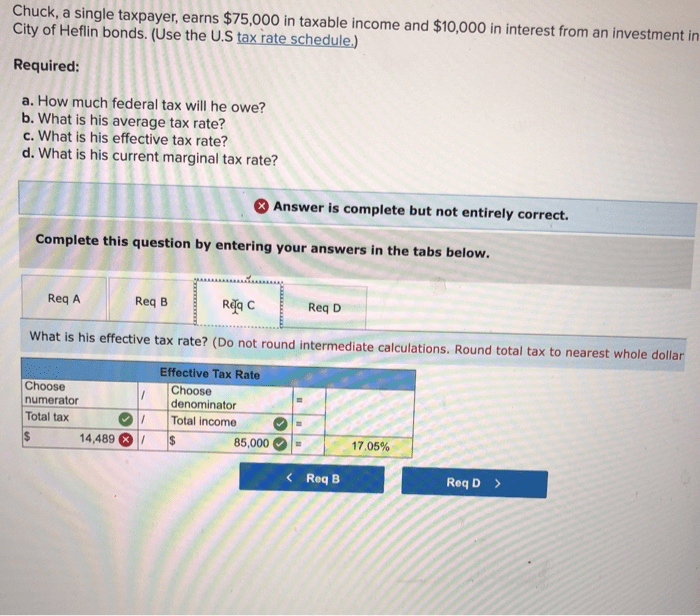
Tax Implications
Single taxpayers with higher incomes will pay more in federal income taxes due to higher tax brackets. Conversely, those with lower incomes will pay less.
Financial Considerations
Individuals with higher incomes may have more disposable income for savings, investments, and discretionary spending. However, they may also face higher living expenses in certain areas.
Those with lower incomes may have limited financial resources and may need to prioritize essential expenses. They may also qualify for government assistance programs.
FAQ Insights: Chuck A Single Taxpayer Earns 75000
What are the potential tax deductions and credits that could reduce the tax liability for a single taxpayer earning $75,000?
Potential tax deductions include mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and retirement contributions. Tax credits that may be available include the earned income tax credit, child tax credit, and saver’s credit.
What are some appropriate savings and investment strategies for a single taxpayer earning $75,000?
Consider contributing to a 401(k) or IRA for retirement savings. Invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds to grow wealth over time. Explore high-yield savings accounts or certificates of deposit for short-term savings goals.
How can a single taxpayer earning $75,000 optimize their lifestyle and spending habits?
Create a budget to track income and expenses. Identify areas where spending can be reduced or optimized. Consider increasing income through a side hustle or career advancement. Set financial goals and develop a spending plan to achieve them.